Understanding Mould Temperature Controllers
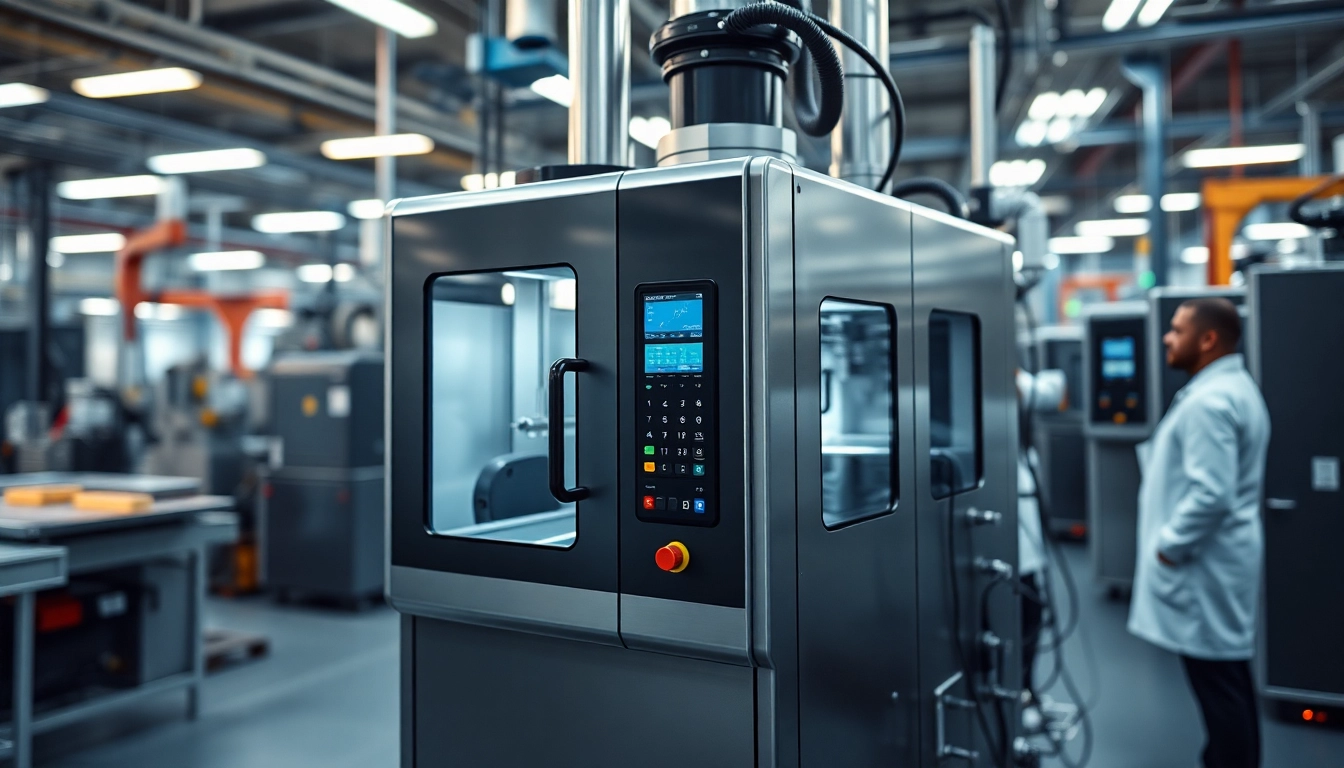
A mould temperature controller is a crucial component in manufacturing processes, particularly in injection molding and thermoplastic production. These controllers are designed to maintain optimal temperature settings for molds during the production cycle, ensuring product quality and uniformity. By regulating the temperature of the mould, manufacturers can achieve better outcomes in terms of product properties and processing efficiency. When exploring options, Mould Temperature Controller systems are pivotal in achieving these goals.
What is a Mould Temperature Controller?
A mould temperature controller is an apparatus that regulates the temperature of a mould to optimize the manufacturing process. It works by circulating a heated or cooled fluid through the mold, maintaining the required temperature for the material being processed. These devices can operate in various temperature ranges, typically from below 0°C to over 350°C, depending on the specific application. The types of fluids used can vary, including water, oil, and specialized temperature control fluids, each selected based on the desired properties and applications.
How Mould Temperature Controllers Enhance Manufacturing
The integration of mould temperature controllers in manufacturing provides several advantages, including:
- Improved Product Quality: Consistent temperature regulation contributes to uniformity in product dimensions and physical properties, minimizing defects.
- Enhanced Cycle Times: Efficient temperature control allows for faster heating and cooling cycles, optimizing production throughput.
- Energy Efficiency: By maintaining the ideal temperature, these devices reduce energy consumption, lowering operational costs.
Key Features of Advanced Mould Temperature Controllers
Modern mould temperature controllers are equipped with various features designed to enhance performance:
- Digital Control Displays: Allow precise monitoring and adjustments to temperature settings.
- PID Control: Proportional-Integral-Derivative controllers offer superior temperature control by adjusting heating and cooling based on real-time data.
- Safety Features: Overheat protection and alarm systems minimize risks associated with equipment failure.
- Remote Monitoring Capabilities: Some advanced models offer integrated IoT features, enabling real-time data analysis and remote adjustments.
Benefits of Precision Temperature Control
Impact on Product Quality and Consistency
The quality of products manufactured using mould temperature controllers is significantly enhanced due to precise thermal management. Inconsistent temperature profiles can lead to problems such as warping, shrinkage, or incomplete filling of the mould, resulting in defective products. With accurate temperature control, manufacturers can produce parts that meet exact specifications, enhancing durability and performance.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Temperature control systems not only improve product quality but also contribute to energy efficiency. By optimizing the heating and cooling processes, manufacturers can reduce energy costs, which is increasingly important in today’s competitive landscape. Efficient systems allow for lower energy demands, resulting in reduced operational costs and a smaller environmental footprint.
Real-World Applications in Various Industries
Mould temperature controllers find applications across diverse industries:
- Plastics Manufacturing: Essential in processes such as injection molding and blow molding.
- Metal Casting: Used to control the temperature of molds for die casting and investment casting.
- Food Industry: Applied in the production of food packaging materials where temperature control affects product safety and quality.
- Electronics: Ensures consistent thermal profiles during the manufacturing of electronic components.
How to Choose the Right Mould Temperature Controller
Factors to Consider Before Purchase
When selecting a mould temperature controller, manufacturers should consider:
- Temperature Range: Evaluate the necessary temperature ranges required for the specific application.
- Fluid Compatibility: Ensure that the unit is compatible with the selected heat transfer fluid.
- Control Features: Assess the control technology and automation capabilities available in units.
- Maintenance Requirements: Consider the ease of maintenance and availability of service support.
Comparative Analysis of Leading Brands
Leading brands in the mould temperature controller market include:
- Topstar: Known for its user-friendly designs and robust performance.
- Regloplas: Offers high-end models with advanced PID controllers and energy-efficient designs.
- Mold-Masters: Known for premium quality with innovative integration capabilities.
Each brand brings unique strengths, making it essential to align brand capabilities with specific operational needs and budget constraints.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting
Some common pitfalls include:
- Ignoring specific application requirements, leading to under or over-specification of the controller.
- Neglecting to consider future scalability and integration potential.
- Overlooking after-sales support and warranty conditions.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Proper installation is critical for optimal performance. Follow these steps:
- Preparation: Ensure that all tools and equipment are ready, including a suitable location with necessary utilities.
- Mounting: Securely mount the unit following manufacturer guidelines to ensure stability.
- Connection: Connect the fluid lines, ensuring no leaks are present.
- Electrical Connections: Follow electrical diagrams to connect power supply safely.
- Testing: Conduct a system check before full operation to ensure all components function correctly.
Regular Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Maintaining your mould temperature controller ensures longevity and reliability:
- Regularly check for leaks in fluid lines and fix them immediately.
- Clean the unit periodically to prevent dust buildup.
- Monitor fluid levels and quality; replace fluids as necessary.
- Schedule professional inspections every year to ensure peak performance.
Diagnostic Procedures for Common Issues
Diagnostic procedures can help troubleshoot common issues:
- Temperature Fluctuations: Check sensor calibration and connections.
- Insufficient Heating: Inspect the heating element and verify fluid circulation.
- Alarms Triggering: Review the manual for alarm codes and troubleshoot accordingly.
Future Trends in Mould Temperature Control Technology
Innovations to Expect by 2025
As technology evolves, we can expect several innovations:
- Smart Temperature Control: Implementation of AI and machine learning for predictive temperature management.
- IoT Integration: Enhanced connectivity for real-time data analysis and remote monitoring of temperature controls.
- Sustainable Technologies: Development of eco-friendly fluids and energy-efficient systems.
Integration with Smart Manufacturing Systems
Integration with Industry 4.0 systems will enhance operational efficiency by using data analytics to optimize temperature controls based on real-time production parameters. This integration will lead to precise adjustments that enhance both quality and efficiency.
Predictions for Market Growth and Technology Adoption
The market for mould temperature controllers is expected to grow steadily, driven by rising demand for quality products and increased automation in manufacturing processes. As companies continue to adopt advanced technologies, the reliance on sophisticated temperature control systems will only increase, making them a cornerstone of modern manufacturing strategies.